Health and Nutritional Information Today
|
|
|
1. Prevention. Diets, Diet plans, foods and dietary supplements that provide health management
 through disease and symptom prevention.
Health conditions
are preventable through nutritional information about those conditions and measures you can take to either heal or prevent. Prevention is always the best medicine.
I want to help you, "Feed a man a fish and you have feed him for a day, teach a man how to fish
and you have feed him for life". If you are overweight and/or obese most people just want to sell you a bigger chair,
I want to show you a healthier and better way. through disease and symptom prevention.
Health conditions
are preventable through nutritional information about those conditions and measures you can take to either heal or prevent. Prevention is always the best medicine.
I want to help you, "Feed a man a fish and you have feed him for a day, teach a man how to fish
and you have feed him for life". If you are overweight and/or obese most people just want to sell you a bigger chair,
I want to show you a healthier and better way.
 2. Performance. Whether you are body building, needing sports nutrition or exercising for good health we are all about finding nutritional products
that provides health enhancement through improved physical and mental condition.
2. Performance. Whether you are body building, needing sports nutrition or exercising for good health we are all about finding nutritional products
that provides health enhancement through improved physical and mental condition.
The focus is on daily health, accomplishment and success.
3. Wellness.
Wellness benefits are about feeling good and finding balance.
This is a holistic approach to health care that includes the body,
mind and spirit through meditation to finding balance in mind, body and spirit. The focus is on daily health needs, MODERATION (we have to long overconsumed)
and variety.
 4. Nurturing. Foods that can supply a sense of caring for the health and quality of life for yourself and others and the associated sense of satisfaction
for the caregiver. Marketing a product from this platform would include a focus on growth and development, aging and healing. Nurturing yourself and others and nurturing
the environment around you. Environmentally friendly products for the inside and well as the outside. From the things we eat to the things we wear, they
all have an impact on the world we live.
4. Nurturing. Foods that can supply a sense of caring for the health and quality of life for yourself and others and the associated sense of satisfaction
for the caregiver. Marketing a product from this platform would include a focus on growth and development, aging and healing. Nurturing yourself and others and nurturing
the environment around you. Environmentally friendly products for the inside and well as the outside. From the things we eat to the things we wear, they
all have an impact on the world we live.
 5. Cosmetics. Cosmetics, how we look and feel about ourselves, benefits women's health and men's health. Looking good and enhancing self-esteem through
improved physical condition and personal appearance are corner stones to good health.
No matter
how well you eat if you have low self esteem, are worried or upset then the body gets out of balance.
5. Cosmetics. Cosmetics, how we look and feel about ourselves, benefits women's health and men's health. Looking good and enhancing self-esteem through
improved physical condition and personal appearance are corner stones to good health.
No matter
how well you eat if you have low self esteem, are worried or upset then the body gets out of balance.
|
|
Healthy HeartHeart Health and Cardiovascular Health – What You Need To Know To Maintain a Healthy Heart
While often thought of as the same thing, heart and cardiovascular disease are different, involving different parts of your body.
· Heart disease refers only to diseases of the heart and the blood vessel system within the heart.
· Cardiovascular disease refers to diseases of the heart and diseases of the blood vessel system (arteries, capillaries, veins) within a person's entire body, such as the brain, legs, and lungs. "Cardio" refers to the heart and "vascular" refers to the blood vessel system.
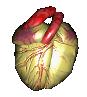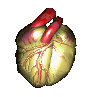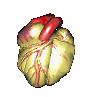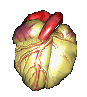 A healthy heart is a strong, muscular pump slightly larger than your fist. When heart health is good, it pumps blood continuously through the circulatory system, the network of elastic tubes that allows blood to flow throughout your body. The circulatory system includes two major organs, the heart and lungs, and blood vessels (arteries, capillaries, and veins). Arteries and capillaries carry oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood from the heart and lungs to all parts of the body. Veins carry oxygen and nutrient-depleted blood back to the heart and lungs. Heart and blood vessel problems do not happen quickly. Over time, the arteries that bring blood to the heart and brain can become blocked from a buildup of cells, fat, and cholesterol (plaque). Poor cardiovascular health results in reduced blood flow to the heart from blockages in the arteries which can cause heart attacks. Lack of blood flow to the brain from a blood clot, or bleeding in the brain from a broken blood vessel, causes a stroke.
A healthy heart is a strong, muscular pump slightly larger than your fist. When heart health is good, it pumps blood continuously through the circulatory system, the network of elastic tubes that allows blood to flow throughout your body. The circulatory system includes two major organs, the heart and lungs, and blood vessels (arteries, capillaries, and veins). Arteries and capillaries carry oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood from the heart and lungs to all parts of the body. Veins carry oxygen and nutrient-depleted blood back to the heart and lungs. Heart and blood vessel problems do not happen quickly. Over time, the arteries that bring blood to the heart and brain can become blocked from a buildup of cells, fat, and cholesterol (plaque). Poor cardiovascular health results in reduced blood flow to the heart from blockages in the arteries which can cause heart attacks. Lack of blood flow to the brain from a blood clot, or bleeding in the brain from a broken blood vessel, causes a stroke.
Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis (or thickening and hardening of the arteries). As we age, some hardening of the arteries can
occur naturally. When a person has atherosclerosis, the inner walls of the arteries become narrower due to a buildup of plaque. Plaque results from deposits
of fat, cholesterol, and other substances. Blood clots form, blocking blood flow, which can lead to heart attacks and strokes. High blood cholesterol,
smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, and not being physically active all put you at greater risk for atherosclerosis.
Coronary heart disease (or coronary artery disease). Coronary heart disease, the most common form of heart disease, affects the blood vessels
(or coronary arteries) of the heart. It causes angina (chest pain) and heart attacks. Women over the age of 40 are more at risk for this disease
because heart-related problems tend to increase with age. And, black women are more likely to die of coronary heart disease than are white women.
The good news is that you can do something about preventing this disease. High blood pressure and cholesterol, smoking, obesity, and not being
physically active all put you at greater risk for coronary heart disease.
Angina. A pain or discomfort in the chest that happens when some part of the heart does not receive enough blood. It feels like a pressing or
squeezing pain, often in the chest under the breastbone, but sometimes in the shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back. The most common trigger for
angina is physical exertion. Other triggers can be emotional stress, extreme cold or heat, alcohol, and smoking. Angina seldom causes permanent
damage to the heart, like a heart attack can. A heart attack happens when the blood flow to a part of the heart is suddenly and permanently cut off.
Stroke. Lack of blood flow to the brain from a blood clot, or bleeding in the brain from a broken blood vessel, causes a stroke. Without a good blood supply,
brain cells cannot get enough oxygen and begin to die. You can also have what are sometimes called "mini strokes," or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs),
where no damage is done to the brain. But even though they do no damage, TIAs are serious and can put you at higher risk of having a full stroke. Not
controlling high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes all increase your risk for stroke.
High blood pressure (or hypertension). There are ways to measure blood pressure and medications to treat high blood pressure (by lowering it).
A blood pressure reading measures the force of blood pumped from the heart against the walls of your blood vessels. It is recorded as two numbers:
a top number of systolic pressure, or the pressure of blood in the vessels as the heart beats; and a bottom number of diastolic pressure, or the
pressure of the blood between heart beats (when the heart rests). Although the average blood pressure reading for adults is 120/80, a slightly
higher or lower reading (for either number) may not be a problem. High blood pressure is diagnosed when the reading consistently exceeds 140/90.
It is often called a "silent" killer because it usually has no signs or symptoms. High blood pressure can cause heart failure in women, and can
also lead to stroke, kidney failure, and other health problems. More than half of all women over age 55 suffer from this serious condition. And,
it is more common and more severe in black women. Talk to your health care provider and get your blood pressure monitored regularly. If you have
high blood pressure, diet, exercise, and medicine can help you to lower and control your blood pressure.
What increases my chances for getting heart and cardiovascular disease?
...
Continue reading about Healthy Heart
|



